Humans have been farming crops for millennia – but the goal remains the same: to feed people. Of course, farming practices have advanced dramatically in the past few centuries, and global pressures continue to drive rapid change in the industry.
Reinout de Heer, Global Product Manager Allium, explores three key trends shaping crop farming and discusses how Hazera’s expertise is paving the way for a more sustainable industry future.
- Mechanization momentum
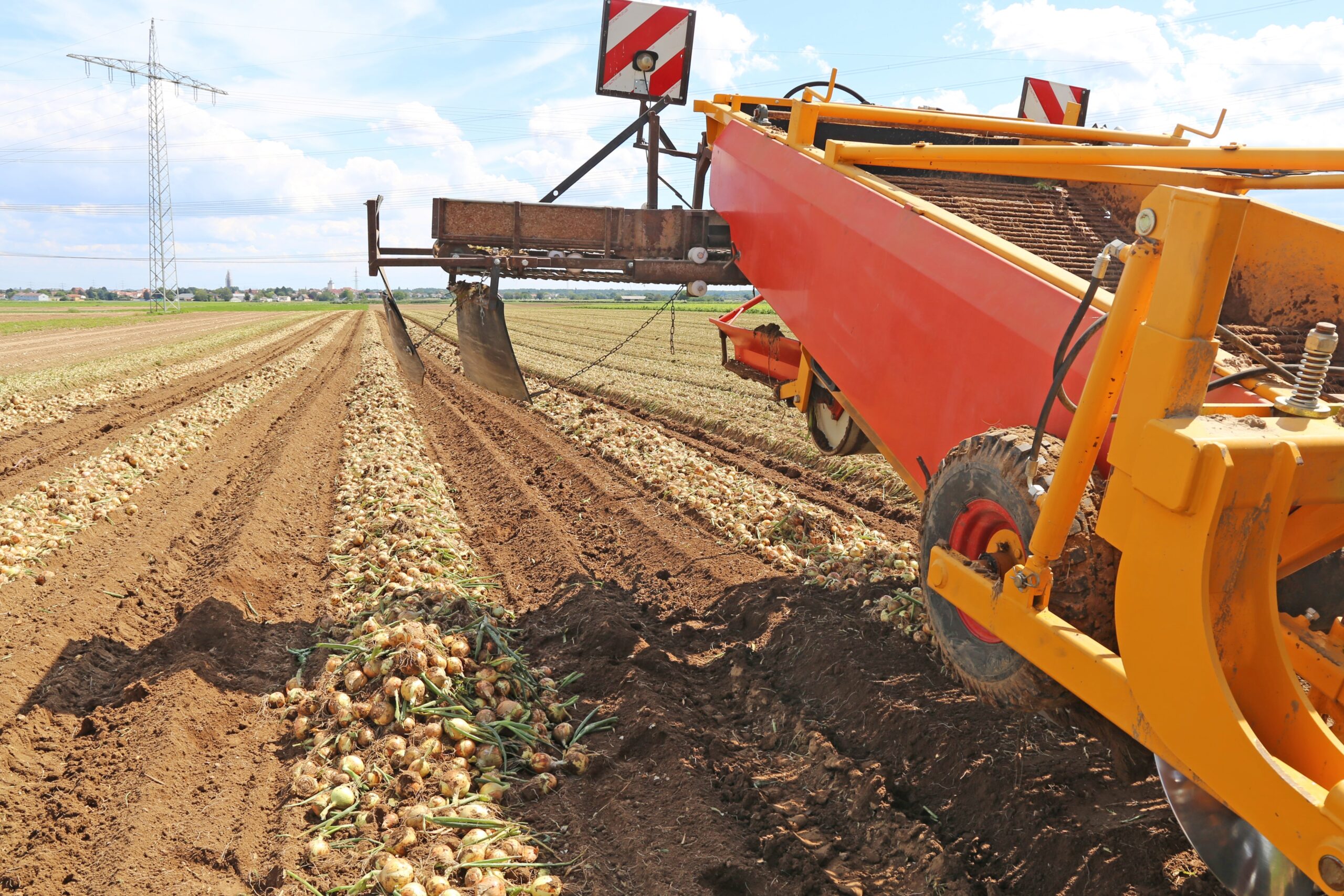
Higher labor costs and decreasing labor availability are leading many farmers to consider mechanical harvesting and other new technologies.
We’re seeing mechanization trends take hold in places like the Netherlands, the UK, and California, in relation to a wide range of produce. However, with crops such as onions, it’s clear that hand-harvesting means a higher quality product with less damage.
This is what makes research into developing new varieties so important. At Hazera, we’re working to test new crop varieties to ensure farmers can invest in the technologies they need, knowing their harvest won’t suffer.
- Chemical control compliance
With tightening environmental regulation, many growers are looking for alternatives to traditional pesticides and fungicides.
Biostimulants are a popular option for Hazera’s customers, being applied to seeds to make plants stronger and more resistant to disease. Product quality can also be boosted through seed pelleting, which creates more rounded seeds, and priming, which means up to five days’ less germination time in the field.
- Local logic
Harvested crops have long been shipped around the world; however, increases in container transport costs are putting pressure on global food systems. Environmental awareness is meanwhile on the rise, as ‘buy local’ or ‘eat seasonal’ become important consumer trends.
At Hazera, we help farmers achieve year-round production with varieties that have good storability and shelf-life properties. Developments in leeks, for instance, which traditionally deteriorate quickly once harvested, are making a big difference. More flexible crop varieties can help customers reduce transport costs, carbon emissions, and food waste, all at once.
Support from the ground up
Around the world, Hazera works in close cooperation with farmers of all kinds of crops to respond effectively to emerging trends. Through trials and other research, we address the industry’s most pressing challenges and develop seed solutions to help agriculturalists – and their plants – thrive.
Want to learn more? Contact us today to see how we can support you!